We were recently sent a ¼ inch tape by Ed Bates that included recordings from the Couriers Folk Club in Leicester, which ran from Autumn 1964 – June 1974.
The tape features performances from The Couriers (Jack Harris and Rex Brisland), George and Thadeus Kaye, Bill Pickering, Mark Newman and Mick Odam.
Jack Harris, who alongside Rex Brisland ran the club, describes how ‘traditional singers like Bert Lloyd, Ewan MacColl and Pete Seeger, Bob Davenport were regular visitors together with ageing ploughboys, miners and fishermen who were often so infirm or unlikely to make their own way to Leicester they had to be fetched by car.’
As well as supporting grassroots folk music from the local area, well known performers such as musical superstar Barbara Dickson, Paul Simon and Joni Mitchell graced the stage.
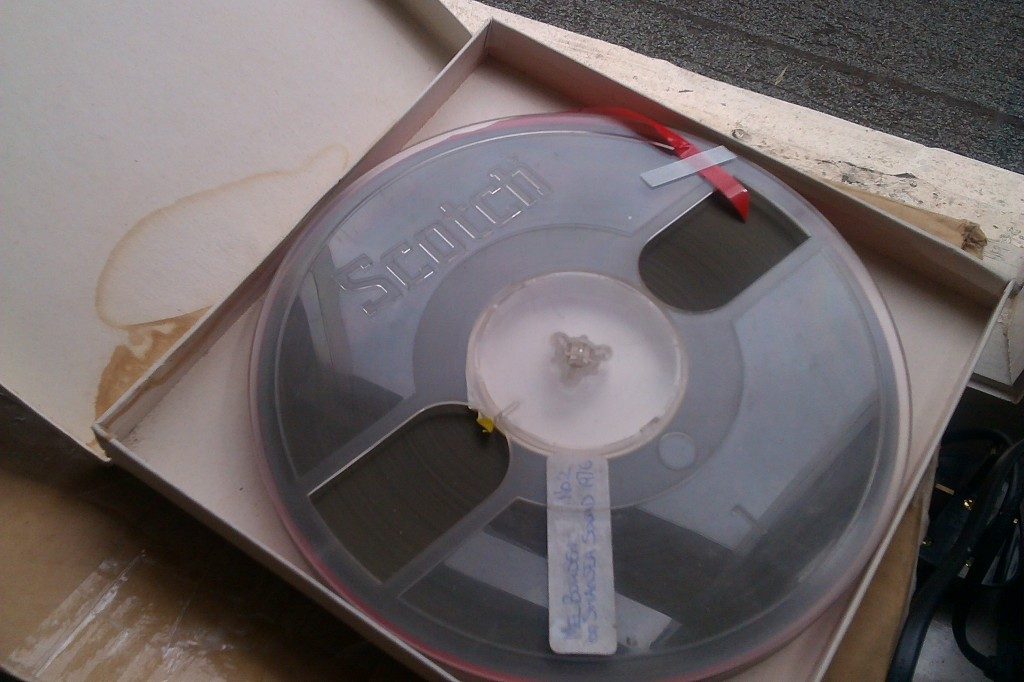
The tape recordings we received span five years. The first recording was made on 6 August 1966, then 3 September 1966, 8 February 1970 and finally 9 April 1971.
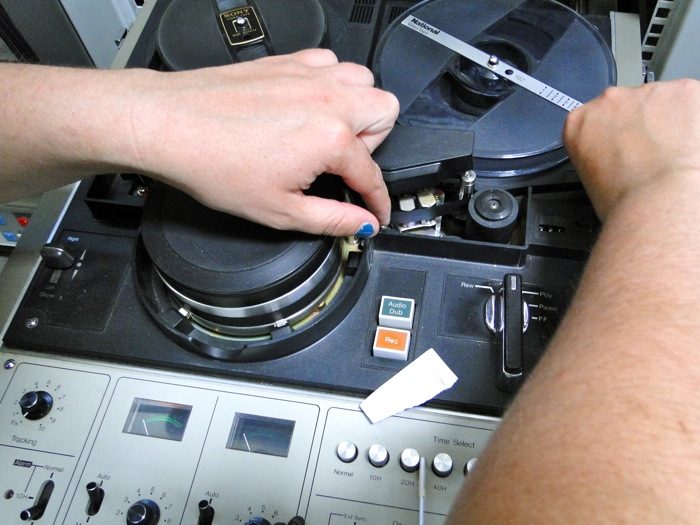
Each performance was recorded on a separate track in mono. This means that the 7” long spool contains 8 hours of music!
Like today’s MP3 digital files, the quality of the recorded sound is compromised because so much information is squeezed into a smaller space on the tape. A better quality recording would have been made if all four channels were used for a single performance, rather than one track for each performance.
The speed at which recordings were made also effects the quality of the recordings, simply because you can record more information per second at a faster rate. The tapes we were sent were recorded at 7 ½ per second on what is likely to have been a domestic tape recorder such as the Sony TC-263D. Ed’s letter to us speaks volumes about the conditions in which the recordings were made:
‘I was present at the Couriers Folk Club in Leicester when they were recorded so I can say that the recording quality is not good. The Sony recorder was used as an amplifier and on some occasions (if someone remembered) a tape was recorded.’
While the recordings certainly would have benefited from less haphazard recording conditions, the quality of the transfer is surprisingly crisp, as you can hear from this excerpt.
Excerpt from the digitised recordings of the Couriers folk club
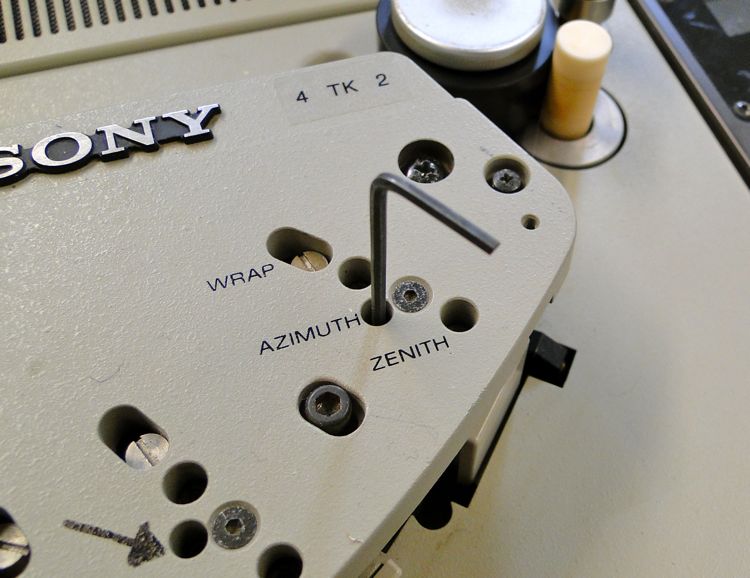
The tape was in good condition, as Philips magnetic reel-to-reel tape often survives well over time, which aided a good transfer. One thing we were especially attentive to in the transfer process was carefully adjusting the azimuth, because of the slow speed of the original recording and the narrow track width.
Image taken from the BASF magnetic tape manual that illustrates how four tracks can be recorded on magnetic tape
The emergence of recordings of the Couriers Club is especially timely given the recent launch of the English and Folk Dance Society‘s The Full English online digital archive . This contains a massive 44,000 records and over 58,000 digitised images about English folk history.
With a dozen or more tapes recently found from the Club, we look forward to helping this unique part of cultural heritage become accessible again.