Greatbear have recently worked with the British Stand Up Comedy Archive (BSUCA) to reformat a number of Digital Audio Tapes (DATs) and U-Matic video tapes from their collection.
Established in 2013 and based at the University of Kent’s Special Collections, the BSUCA aims ‘to celebrate, preserve, and provide access to the archives and records of British stand-up comedy and stand-up comedians.’

In 2014 the BSUCA became one of the University of Kent’s 50th anniversary ‘Beacon Projects‘.
Beacon Project funding will support work to ‘catalogue, preserve, digitise, and make accessible the existing collections, and identify new relevant collections.’
They will also hold a number of events which engage comedians ‘in conversation’ about their archives, excerpts from these events are documented here.
We are honoured that project archivist Elspeth Millar took time out of her busy archiving schedule to tell us a bit more about the BSUCA.
She told us:
‘I’m really enjoying the variety of material that I get to work on, including printed material (posters, flyers, letters, notebooks), audio-visual material on a range of formats (audio cassettes, VHS, DAT, MiniDisc, U-matic), and also born-digital records held on obsolete formats (such as 3.5” floppy disks).
In addition the content of the material is, of course, really interesting, and I feel that I am learning a lot from our collections, including about the history of stand-up comedy (from the alternative cabaret movement, to alternative comedy, to the comedy ‘industry’ today) but also political and social topics (for example Mark Thomas’ collection includes a lot of material on the arms trade and large corporations). We are also holding events with some fantastic comedians (Richard Herring, Stewart Lee, Mark Thomas, and at the Edinburgh Festival Fringe, Jo Brand, Alexei Sayle, Susan Calman) so it is wonderful to hear comedians themselves reflecting on their work and on material that they have deposited with the archive.’
You can keep up to date with the latest news from the BSUCA archive on twitter and view images from their collections on flickr.
Read on for more from Elspeth. Her answers cover issues such as selection and appraisal decisions, metadata and dissemination plans for the BSUCA.
They also provide useful insight into the digital preservation tools BSUCA use to manage their digitised and born-digital assets.
Once again, massive thanks to her for responding to our questions and best of luck to BSUCA in the future.
BSCUA Responses to Greatbear Questions
1. What motivated you to get the tapes you sent to us re-formatted now? i.e., what kinds of selection and appraisal processes were behind the decision?
The British Stand-Up Comedy Archive has AV material on a number of audio and moving image formats, magnetic and optical, including audio compact cassettes, MiniDiscs, DATs (Digital Audio Tapes), VHS, DVCams, Audio CD and U-matic tapes. None of these formats are suitable for archival storage and all material will need to be digitised or transferred from their original carrier to digital files. We can carry out the digitisation (or digital transfer) of some audio in-house and we have started our project by transferring material originally captured or stored on MiniDiscs, Audio CDs, and audio compact cassettes1. After assessing all the formats we currently have it was decided to outsource the digitisation of DATs and U-matic tapes. Both of these are priority formats for transfer from a preservation perspective2 and after some research I learnt that DATs can be problematic to transfer due to ‘DAT compatibility’ and dropout problems3. In addition, we have neither a DAT machine or U-matic machine already within Special Collections or within the University, and with the number of recordings on these formats currently limited, it was felt that it would not make sense to purchase already obsolete equipment, which would then need to be professionally maintained.
The other important reason for transferring the tapes of course was for accessibility, so that we can make the recordings accessible to researchers. In addition, our funding is currently only for one year4, so it is vital to ensure that audio-visual material on obsolete formats are transferred during this first phase of the project.
2. Can you tell us how metadata helps you to describe, preserve and aid discovery of the Stand Up Comedy archive.
Providing information about our audiovisual items (and resulting digital items) is incredibly important from both an access and preservation perspective. Metadata about analogue items (and subsequent digital files) and born-digital files will be included in the cataloguing collections management system used by the British Stand-Up Comedy Archive (which is part of the University of Kent’s Special Collections & Archives). The catalogue records will include descriptive metadata and administrative metadata. Metadata which comes under the ‘descriptive metadata’ heading describes the item/file and includes a summary of the contents of the recording, all of which helps to make recordings discoverable for researchers. This metadata is also vital from a preservation perspective as it allows archivists to retrieve and identify files. Metadata which comes under the ‘administrative metadata’ heading provides information to help manage the file(s)/recordings, and includes information related to Intellectual Property Rights (including copyright) and preservation information such as the file format and the digitisation/digital transfer. Researchers will be interested in some of these issues (e.g. copyright, as this determines how archived recordings can be used) but from a digital preservation perspective this metadata is extremely important as it records information about the format of the digital file, information about the original carrier, as well as fixity information, to measure whether the file has changed over time.
This metadata will be recorded in our catalogue and will be searchable via the University of Kent’s website and in the future some archive aggregators. However, we are also experimenting with different processes and tools for embedding metadata in files, and researching different metadata standards for this. The benefits of embedding some metadata within the file include the removal of the risk of losing the link between the metadata and the digital file that it is describing. In addition, metadata embedded in born-digital master and digitised master files can also be transferred to ‘access’ copies (generated at a lower specification/resolution) which will also assist in user accessibility. Embedded metadata has its limitations and it is not that flexible, which is why we are using a dual approach of embedding some metadata, but also keeping this information externally in our catalogue.
3. How do you manage, and plan to manage digital audio and audio visual materials in the Stand Up Archive? What digital preservation tools do you use?
The first process in managing digital AV materials in the BSUCA is to think about the file formats that we will use for long-term preservation and access. For audio material we are digitising as LPCM (Linear Pulse Code Modulation) in a Wave format (.wav) wrapper. The addition of embedding metadata into these wave files extends the file to become BWF .wav files, the standard recommended by the International Association of Audiovisual Archives (IASA).5
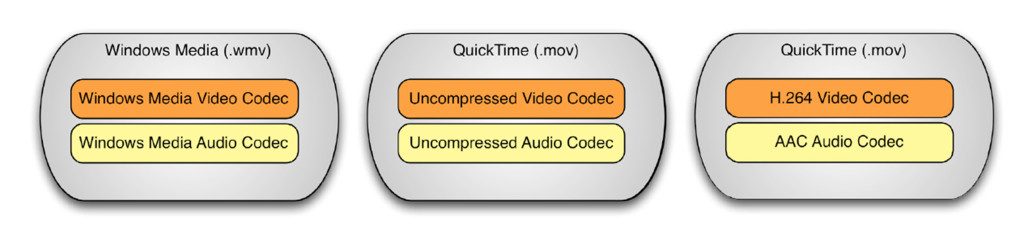
Deciding upon a file format for digitising moving image has been trickier, as the Greatbear team have already written about on this blog; we hope to get underway with digitisation of VHS in September and we are looking at using the FFv1 codec (an open-source lossless compressed codec) wrapped as either AVI or Matroska (MKV).
We are also experimenting with a number of digital preservation tools; one directory that has proved great for discovering such tools is the COPTR wiki (Community Owned digital Preservation Tool Registry), a really useful collated list of various digital preservation tools . One aspect of our digital preservation planning is the creation of checksums as early in the lifecycle of the digital file as possible. We are using a tool called Blackbush, which is a checksum tool6 which generates MD5 hash files which was developed for the British Library’s Sound Archive. To embed metadata into .wav files we are using the BWF MetaEdit tool, a free open-source tool developed by AV Preserve and the Federal Agencies Digitization Guidelines Initiative. When our archival master is a compressed format (such as an mp3 on a data or audio CD which has been deposited), we are using tools such as Adobe Bridge to embed metadata in the ID3 format (or Adobe Audition’s metadata tools as we transfer audio). The advantage of BWF MetaEdit for wav files is that it is a free open-source tool, which also has other functions such as batch editing (we can edit multiple wav files at once) and batch import and export functions, which will be useful for when we catalogue this material to item level.
Other tools that we have found useful include DROID (Digital Record Object Identification), developed by The National Archives, and, for other digital material we are using forensic imaging tools such as FTK Imager and ImDisk to mount virtual images of disk images.
4. How do you think the material will be used by future researchers? As a Stand Up Archive I imagine you get a lot of requests for material from broadcasters. How do you manage requests and expectations from different user communities?
The British Stand-Up Comedy Archive is still in its infancy; although we have had material since 2013, it has only been since the beginning of this year that we have been funded to digitise and preserve the material already deposited, start to catalogue it, make it accessible, and publicise what we have and what we are aiming to do.
But two of our core purposes are to ensure access (that these archives are universally discoverable and accessible), and to ensure that the archives are used, and used in a variety of ways (popular culture, academic research, teaching, journalism, general enjoyment). Our main user group at the moment is actually students studying stand-up and popular performance at the University of Kent (at BA and MA level) who have used AV material as part of their course, and we also have a number volunteering with the project, doing summaries of recorded interviews and stand-up performances.
Notes
[1] We have purchased an audio cassette deck (Denon DN-790R) and are using a MiniDisc deck on loan from colleagues within the University, and have also purchased an external audio capture card/A-D converter.
[2] https://psap.library.illinois.edu/format-id-guide/audiotape#dat and https://psap.library.illinois.edu/format-id-guide/videotape#umatic.
[3] https://siarchives.si.edu/sites/default/files/pdfs/digitalAudioTapesPreservation2010_0.pdf (page 5-8) and http://thegreatbear.co.uk/audio-tape/transferring-dats-to-digital-files/.
[4] The British Stand-Up Comedy Archive is part of the University of Kent’s Special Collections and Archives, but it currently has specific funding for one year (as a Beacon Project) to digitise and make accessible its current holdings; more about the Beacon projects can be found at http://www.kent.ac.uk/beacon/about.html.
[5] Guidelines on the Production and Preservation of Digital Audio Objects, IASA-TC 04, 2.8.2
[6] A checksum is ‘an algorithmically-computed numeric value for a file or a set of files used to validate the state and content of the file for the purpose of detecting accidental errors that may have been introduced during its transmission or storage. The integrity of the data can be checked at any later time by recomputing the checksum and comparing it with the stored one. If the checksums match, the data was almost certainly not altered’. National Digital Stewardship Alliance Glossary, http://www.digitalpreservation.gov/ndsa/ndsa-glossary.html.