introduction to VHS, S-VHS, VHS-C & D-VHS cassette transfer
The Video Home System (VHS) cassette format dominated the domestic video tape market globally, from when it was launched in 1976 to its decline around 1996. Consequently there is a huge range of content stored on VHS tapes that is at risk of loss.
At Greatbear, we digitise VHS, S-VHS, VHS-C and D-VHS video tape recordings, in PAL, NTSC, and SECAM, at standard play (SP), long play (LP) and extra long play (ELP) speeds, where appropriate.
We offer a range of delivery formats for our video transfers. Following International Association of Sound and Audiovisual Archives TC-06 guidelines, we deliver FFV1 lossless files or 10-bit uncompressed video files in .mkv or .mov containers for archives. We can also produce Apple ProRes mezzanine files for ease of editing. We provide smaller viewing files as H.264 encoded .mp4 files or on DVD. We're happy to create any other digital video files, according to your needs.
We can provide the appropriately-sized USB delivery media for your files, or use media supplied by you, or deliver your files online. Files delivered on hard drive can be for any operating system MacOS, Windows or GNU/Linux and filesystems (HFS+, NTFS or EXT3).
VHS video cassette recordings can vary both in duration and in the extent of physical tape degradation, so we always assess tapes before confirming the price of a transfer.
We offer free assessments - please contact us to discuss your project.
For an introduction to our assessment and treatment processes, please see our guide to "what happens to your video tape".
VHS, S-VHS, VHS-C & D-VHS machines
While VHS isn't as threatened by machine obsolescence as some formats, due to its worldwide popularity: not all machines were made equal. VHS video tape recorders were designed and built for all markets and prices - choosing the appropriate machines can make a significant difference to the stability and image quality for this format.
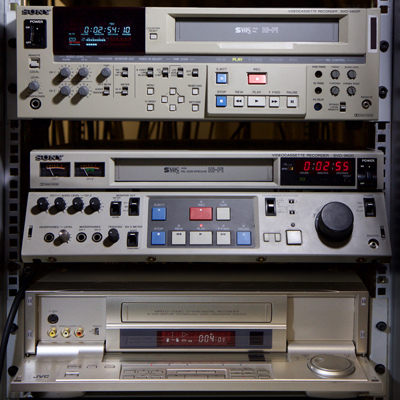
We use a combination of professional and domestic models chosen for their features, replay quality, ability to replay a range of recording variations and their ability to be repaired and serviced in the long term.
We use Sony SVO-5800 for PAL, standard play (SP) recordings and JVC S-VHS and D-VHS machines for LP and ELP recordings. We do have a wide range of VHS and S-VHS machines which can be used for larger projects / particular types or problematic tapes.
Our studio machines include:
- Mitsubishi BV-2000 x 2
- Panasonic AG-MD835 x 4
- Panasonic AG-4700 x 2
- Panasonic AG-7150
- Panasonic AG-7750 x 2
- Panasonic AG-8700
- Panasonic NV-V8000 x 3
- Panasonic AG-TL350 time lapse CCTV VTRs x 5
- JVC BR-S522 with TBC / DNR options installed
- JVC SR-VS20 x 2
- JVC HR-DVS3 EK x 2
- JVC HR-S7600 x 2
- JVC HM-DR10000 D-VHS
- Sony SVO-5800P x 2
We also hold a range of spares and backup machines for the future.
VHS, S-VHS, VHS-C & D-VHS format variation
| VHS tape type | video standard | standard play (SP) speed supported | long play (LP) speed supported | extra long play (ELP) speed supported | 12h / 24h timelapse security speed supported | parallel capture of longitudinal & hi-fi audio as separate stereo tracks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VHS | PAL | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| VHS-C | PAL | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| S-VHS | PAL | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| D-VHS | PAL | ✓ | ✓ (LS3 Mode) | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| VHS | PAL-N | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| VHS-C | PAL-N | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| S-VHS | PAL-N | n/a | n/a | n/a | ✗ | ✗ |
| D-VHS | PAL-N | n/a | n/a | n/a | ✗ | ✗ |
| VHS | NTSC / M-PAL | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| VHS-C | NTSC / M-PAL | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| S-VHS | NTSC / M-PAL | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| D-VHS | NTSC / M-PAL | ✓ | ✓ (LS3 Mode) | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| VHS | SECAM / MESECAM | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| VHS-C | SECAM / MESECAM | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| S-VHS | SECAM / MESECAM | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| D-VHS | SECAM / MESECAM | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
Scroll to the right to view full table on smaller screens.
VHS, S-VHS, VHS-C & D-VHS tape risks & vulnerabilities
VHS tapes can suffer from problems that affect other video tapes, but being a very common domestic format, they do tend to be mistreated in unusual ways more often.
Most domestic brands of VHS tape tend to not suffer from binder hydrolysis or sticky shed syndrome, so rarely need baking. Some brands aimed at the professional market, especially S-VHS types, have back-coating so can suffer, but this isn't that common in our experience.
Broken, smashed, mould-infested and water-damaged tapes are more common though, and careful re-shelling, cleaning and sometimes unsticking of the tape layers is necessary before replay can be attempted.
We have the VHS model of RTI Tapechek machine that's designed to clean and burnish the tape surface while also checking for damage. This can be useful occasionally but it's not appropriate for all tape problems and can, in some instances, cause more damage.
Given the worldwide popularity of the VHS format we can also replay and digitise TV standards less common in the UK and the slower recording speeds sometimes used too.
A common issue with VHS recordings is the soundtrack used. As the format evolved, a higher-quality, stereo soundtrack was possible in addition to the mono, linear soundtrack. Sometimes the HiFi soundtrack can suffer with noticeable audio dropouts. We can preserve both soundtracks in these cases so the linear soundtrack is still available and in sync when the HiFi soundtrack becomes problematic. Domestic VTRs will constantly switch between soundtracks which sounds odd and usually don't allow separated soundtracks.
VHS, S-VHS, VHS-C & D-VHS history
VHS was developed by JVC in the early 1970s, and launched in Japan in 1976 and the US & UK in 1977. By the mid 1980s it had become the dominant system for domestic analogue video recording on tape cassettes.
S-VHS, launched in 1987, improved picture quality by increasing the horizontal luminance resolution to 420 lines per picture height (from 240 lines for VHS).
VHS-C was a compact form of VHS, launched by JVC in 1982 primarily for use in consumer-level analog recording camcorders.
D-VHS (Digital VHS, formerly Data VHS) was a digital video recording format developed by JVC, in collaboration with Hitachi, Matsushita, and Philips, and released in 1998.
Video cassettes, tape boxes, compatible cameras and playback machines for VHS, S-VHS, VHS-C and D-VHS can be identified by these logos. VHS is a trademark of JVC.